Segmenting data
The qim3d library provides a set of methods for data segmentation.
qim3d.segmentation.watershed
watershed(binary_volume, min_distance=5)
Apply watershed segmentation to a binary volume.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Default |
binary_volume
|
ndarray
|
Binary volume to segment. The input should be a 3D binary image where non-zero elements
represent the objects to be segmented.
|
required
|
min_distance
|
int
|
Minimum number of pixels separating peaks in the distance transform. Peaks that are
too close will be merged, affecting the number of segmented objects. Default is 5.
|
5
|
Returns:
| Name | Type |
Description |
labeled_vol |
ndarray
|
A 3D array of the same shape as the input binary_volume, where each segmented object is assigned a unique integer label.
|
num_labels |
int
|
The total number of unique objects found in the labeled volume.
|
Example
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
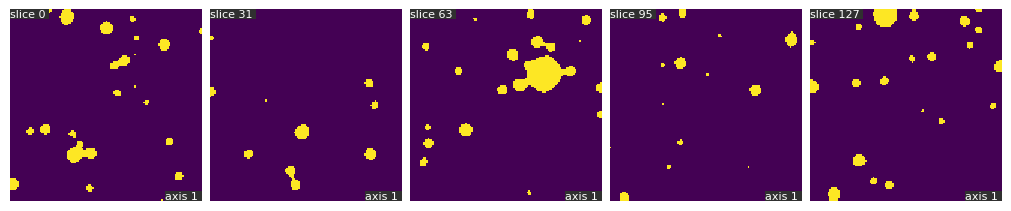
binary_volume = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma = 2)<60
fig1 = qim3d.viz.slices_grid(binary_volume, slice_axis=1, display_figure=True)

labeled_volume, num_labels = qim3d.segmentation.watershed(binary_volume)
cmap = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(num_labels)
fig2 = qim3d.viz.slices_grid(labeled_volume, slice_axis=1, color_map=cmap, display_figure=True)

Source code in qim3d/segmentation/_common_segmentation_methods.py
| def watershed(binary_volume: np.ndarray, min_distance: int = 5) -> tuple[np.ndarray, int]:
"""
Apply watershed segmentation to a binary volume.
Args:
binary_volume (np.ndarray): Binary volume to segment. The input should be a 3D binary image where non-zero elements
represent the objects to be segmented.
min_distance (int): Minimum number of pixels separating peaks in the distance transform. Peaks that are
too close will be merged, affecting the number of segmented objects. Default is 5.
Returns:
labeled_vol (np.ndarray): A 3D array of the same shape as the input `binary_volume`, where each segmented object is assigned a unique integer label.
num_labels (int): The total number of unique objects found in the labeled volume.
Example:
```python
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary_volume = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma = 2)<60
fig1 = qim3d.viz.slices_grid(binary_volume, slice_axis=1, display_figure=True)
```
```python
labeled_volume, num_labels = qim3d.segmentation.watershed(binary_volume)
cmap = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(num_labels)
fig2 = qim3d.viz.slices_grid(labeled_volume, slice_axis=1, color_map=cmap, display_figure=True)
```

"""
import scipy
import skimage
if len(np.unique(binary_volume)) > 2:
raise ValueError(
'binary_volume has to be binary volume - it must contain max 2 unique values.'
)
# Compute distance transform of binary volume
distance = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(binary_volume)
# Find peak coordinates in distance transform
coords = skimage.feature.peak_local_max(
distance, min_distance=min_distance, labels=binary_volume
)
# Create a mask with peak coordinates
mask = np.zeros(distance.shape, dtype=bool)
mask[tuple(coords.T)] = True
# Label peaks
markers, _ = scipy.ndimage.label(mask)
# Apply watershed segmentation
labeled_volume = skimage.segmentation.watershed(
-distance, markers=markers, mask=binary_volume
)
# Extract number of objects found
num_labels = len(np.unique(labeled_volume)) - 1
log.info(f'Total number of objects found: {num_labels}')
return labeled_volume, num_labels
|
qim3d.segmentation.connected_components
connected_components(volume, connectivity=1)
Computes connected components of a binary volume.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Default |
volume
|
ndarray
|
An array-like object to be labeled. Any non-zero values in input are
counted as features and zero values are considered the background.
|
required
|
connectivity
|
int
|
Controls the squared distance of connectivity. Can range from 1 to 3.
|
1
|
Returns:
| Name | Type |
Description |
cc |
ConnectedComponents
|
A ConnectedComponents object containing the labeled volume and a number of useful methods and attributes.
|
Example
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.slicer(cc.labels, slice_axis=1, color_map=color_map)
Show the largest connected components
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
filtered = cc.filter_by_largest(5)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.volumetric(filtered, color_map=color_map, constant_opacity=True)
Filter the connected components by size
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
# Show a histogram of the distribution of label sizes
cc.sizes_histogram()
# Based on the histogram, choose a range of sizes
filtered = cc.filter_by_size(min_size=1e2, max_size=2e2)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.volumetric(filtered, color_map=color_map, constant_opacity=True)
Source code in qim3d/segmentation/_connected_components.py
| def connected_components(volume: np.ndarray, connectivity: int = 1) -> ConnectedComponents:
"""
Computes connected components of a binary volume.
Args:
volume (np.ndarray): An array-like object to be labeled. Any non-zero values in `input` are
counted as features and zero values are considered the background.
connectivity (int, optional): Controls the squared distance of connectivity. Can range from 1 to 3.
Returns:
cc: A ConnectedComponents object containing the labeled volume and a number of useful methods and attributes.
Example:
```python
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.slicer(cc.labels, slice_axis=1, color_map=color_map)
```
Example: Show the largest connected components
```python
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
filtered = cc.filter_by_largest(5)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.volumetric(filtered, color_map=color_map, constant_opacity=True)
```
Example: Filter the connected components by size
```python
import qim3d
vol = qim3d.examples.cement_128x128x128
binary = qim3d.filters.gaussian(vol, sigma=2) < 60
cc = qim3d.segmentation.connected_components(binary)
# Show a histogram of the distribution of label sizes
cc.sizes_histogram()
# Based on the histogram, choose a range of sizes
filtered = cc.filter_by_size(min_size=1e2, max_size=2e2)
color_map = qim3d.viz.colormaps.segmentation(len(cc), style='bright')
qim3d.viz.volumetric(filtered, color_map=color_map, constant_opacity=True)
```
"""
cc = ConnectedComponents(volume, connectivity)
return cc
|

